Shoulder arthroplasty is currently the most effective means of treating end-stage glenohumeral osteoarthritis in modern medicine. While over the past decades innovation has created substantial improvements in primary shoulder arthroplasty (rTSA) , it was not until the advent of reverse shoulder arthroplasty that a substantial expansion of the overall indications and applications for shoulder arthroplasty could actually occur. Present day, rTSA has eclipsed primary shoulder arthroplasty as the most commonly performed shoulder arthroplasty procedure worldwide, as the indications have rapidly expanded from treating rotator cuff tear arthropathy to proximal humerus fracture, and irreparable rotator cuff tears to primary osteoarthritis. Despite this rapid growth in indications, innovation in rTSA design has lagged behind—until now.
Exactech’s Equinoxe® Platform Shoulder System has been a market leader in helping surgeons treat patients with an increasing variety of clinical scenarios. By providing a robust number of options in terms of angled augments, as well as variability in offset and lateralization, the Equinoxe System provides a platform arthroplasty solution for surgeons. Until now, a critical limitation of the Equinoxe Reverse System had been the size of the baseplate. Originally based upon dimensions of the larger stature individuals seen in the western world, the standard Equinoxe baseplate has distinct limitations when used for smaller stature patients commonly encountered in Asian populations. With the creation of the Small Reverse Shoulder, rTSA with the Equinoxe System can now be accurately and effectively performed in virtually all anatomy types.
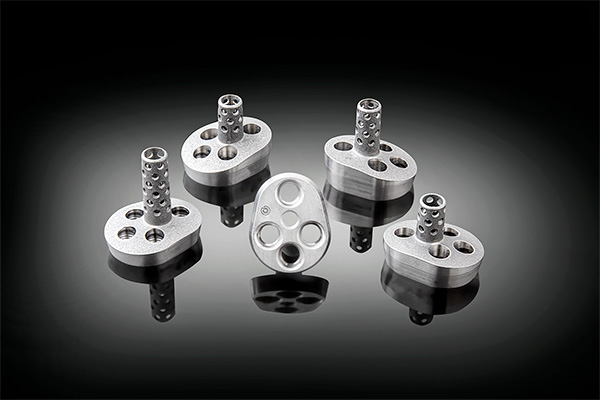

Small-stature and associated small glenoid morphologies have long proven challenging for surgeons interested in performing primary and especially rTSAs. This challenging clinical scenario is a common occurrence in the U.S. rTSA markets but even more critical in the Asian markets. This discrepancy is even more apparent given the difference in clinical presentation of shoulder pathology in Asian populations. The incidence of primary osteoarthritis in Asian populations is exceedingly low. Rather, the most common indication for shoulder arthroplasty in Asian markets is for treatment of rotator cuff tear arthropathy. Indeed, rTSA represents 80% of the shoulder arthroplasty market in Asia.1 Furthermore, this market is growing rapidly with an expected 41% growth rate in China and over 300% growth rate in Korea in the next five years.1,2
With the standard baseplate, fully half of the world’s population has been excluded from the benefits of the Exactech Equinoxe Reverse System. In computer modeling studies of 100 small-stature glenoids, detailed analysis of height, width and vault depth were performed. Results demonstrated substantial size differences compared to the Western population, especially significant in females. With an average glenoid height and width of 33 x 24 mm respectively and a vault depth of less than 15 mm, small-stature females start off with smaller dimensions than the actual standard Equinoxe baseplate.3 With onset of arthritis, erosions and bone loss, the size discrepancy becomes even more pronounced. Indeed, one study examining accuracy of baseplate implantation in Asian glenoids demonstrated that implantation with a standard baseplate had a 33% perforation rate of the bone cage. Of the remaining cases in which the cage remained in the vault, 25% were in suboptimal positioning. Just slightly over 40% were able to be correctly placed.1
The Small Reverse Shoulder has multiple features which may provide for enhanced glenoid fixation.
The new Small Reverse Shoulder and enhanced reverse shoulder system comprise a major evolutionary step for the Exactech Equinoxe platform stem. Using data from the proprietary CT analysis discussed previously, the Equinoxe Small Reverse Shoulder achieves a width dimension similar to competitors on the market yet has expansion capabilities (through augments, glenosphere options and humeral liners) to handle a variety of clinical scenarios in both small and large stature patients. Furthermore, by incorporating key design features of the standard Equinoxe Shoulder System, the team was able to provide the same robust characteristics that have led to over a decade of clinical success. Among these critical elements include enhancements intended to reduce scapular notching, improve glenoid fixation and provide a seamlessly integrated design within the Equinoxe System.
The Equinoxe Reverse Shoulder has been shown to dramatically reduce scapular notching by seven-fold;4,5 the Small Reverse Shoulder design was based on the clinically proven Equinoxe design. The baseplate is anatomically shaped with dimensions of 29.5mm x 23.9mm and is 24.4% smaller than the current Equinoxe baseplate.6 This combination, along with built-in baseplate offset, enables a shift in glenosphere position in an effort to avoid scapular notching while maintaining precise glenoid placement. Furthermore, the elongated glenosphere articular surface and new chamfered sides were designed to facilitate easier insertion, improve inferior offset and increase range of motion. The matching humeral implant retains the same 145-degree neck angle, which enables lateralization of the humerus without lateralizing the center of rotation.
The Small Reverse Shoulder has multiple features which may provide for enhanced glenoid fixation. The implant features the same curved backside as the standard baseplate, designed to minimize bone removal and convert shear forces into stabilizing compressive forces. By maintaining the same central cage diameter but shortening it (13.1mm vs 16.6mm) and shifting it to a slightly more central position, the small reverse baseplate provides initial fixation strength while limiting vault penetration or malposition in smaller glenoid anatomy.6,7 The same variable angle compression screws with locking caps enhance the initial fixation and compression, while unique to the Equinoxe Reverse Shoulder; the central cage with addition of bone graft inserted inside helps to promote bone through-growth and long-term biologic fixation.8 As a result of the smaller size and anatomic shape, the smaller baseplate design allows for greater percent surface area of contact with eroded glenoids such as those with a biconcave pattern. Finally, for more complex glenoid morphology, the baseplate will soon be offered in a superior (10 degrees), posterior (8 degrees) and superior/posterior configuration.
The Small Reverse Shoulder is designed to seamlessly integrate with the entire Equinoxe System. The current 36mm and 40mm glenospheres are available with 0mm and 2.5mm liners and lock into the existing humeral tray system providing full compatibility with the Equinoxe Platform stems. Lateralized versions of both 36 and 40mm glenospheres will be released in 2019 allowing for even greater flexibility with soft tissue balancing, anatomic tensioning of the remaining rotator cuff and improved deltoid wrap. With a wide range of augmented glenoid baseplates available to address various types of glenoid wear, the small reverse baseplate was designed to allow for revision flexibility even in the most limited of bone stock.
The Small Reverse Shoulder system is a game-changing innovation for the Equinoxe Shoulder System. The Equinoxe Reverse Shoulder has long been a leader in reducing scapular notching, providing enhanced glenoid fixation and providing a seamlessly integrated design.9,10 With the addition of the Small Reverse Shoulder, Exactech now sets the industry standard for providing this robust array of features in treating both small and large glenoid morphology. Indeed, with the new Exactech Small Reverse Shoulder, surgeons worldwide will be able to address a wider range of clinical shoulder problems than ever before making sure to have a great day in the O.R.
REFERENCES
- Yamakado, K. (2018). Worldwide Growth of TSA: The Emerging Asian-Pacific Market.
- Tian, L., Radhakrishnan, P. and Archila, D. (2013). MediPoint GlobalData. Total Shoulder Replacement: Global Analysis and Market Forecasts.
- Matsuki, Keisuke, et al. Three-dimensional measurement of glenoid dimensions and orientations. Journal of Orthopaedic Science (2018).
- Mollon, Brent, et al. Impact of scapular notching on clinical outcomes after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: an analysis of 476 shoulders. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery 26.7 (2017): 1253-1261.
- Roche, C. P., et al. Scapular notching and osteophyte formation after reverse shoulder replacement: radiological analysis of implant position in male and female patients. The bone & joint journal 95.4 (2013): 530-535.
- 718-04-45 Equinoxe Small Reverse Shoulder Operative Technique Addendum
- 718-01-30 Equinoxe Platform Shoulder System Operative Technique
- Data on file at Exactech.
- Simovitch, R., et al. (2019). Impact of scapular notching on reverse total shoulder arthroplasty midterm outcomes: 5-year minimum follow-up. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery.
- Mollon, B., et al. (2017). Impact of scapular notching on clinical outcomes after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: an analysis of 476 shoulders. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery, 26(7), 1253-1261.